What is a desulfurizer filtrating system?
A desulfurizer scrubber filtration system is an air treatment plant of integrated components designed to remove hydrogen sulfide (H2S) from biogas. This system typically includes a chemical scrubber, an oxidation tank, and a sedimentation tank. It is specifically engineered to reduce the levels of toxic and corrosive hydrogen sulfide gas, thereby making biogas safer for use and helping to protect equipment from corrosion.
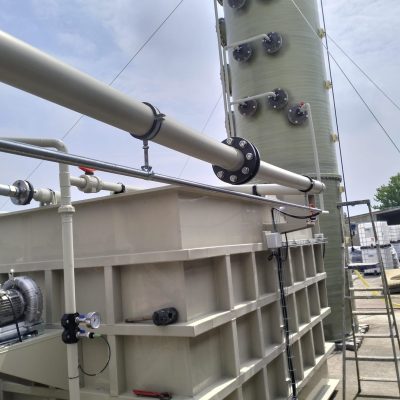
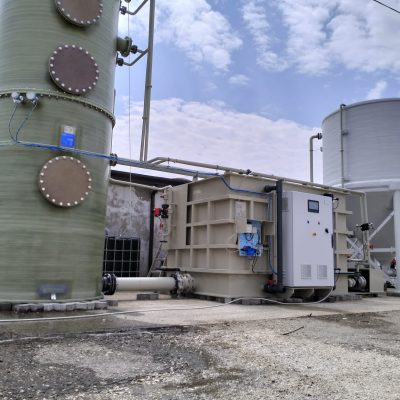
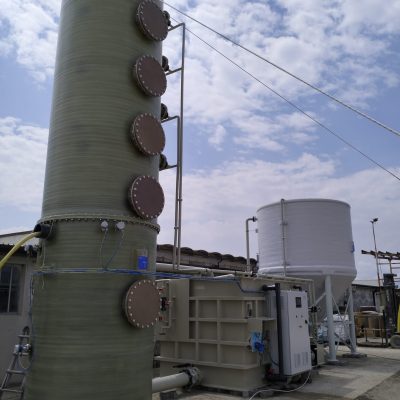




How does it work?
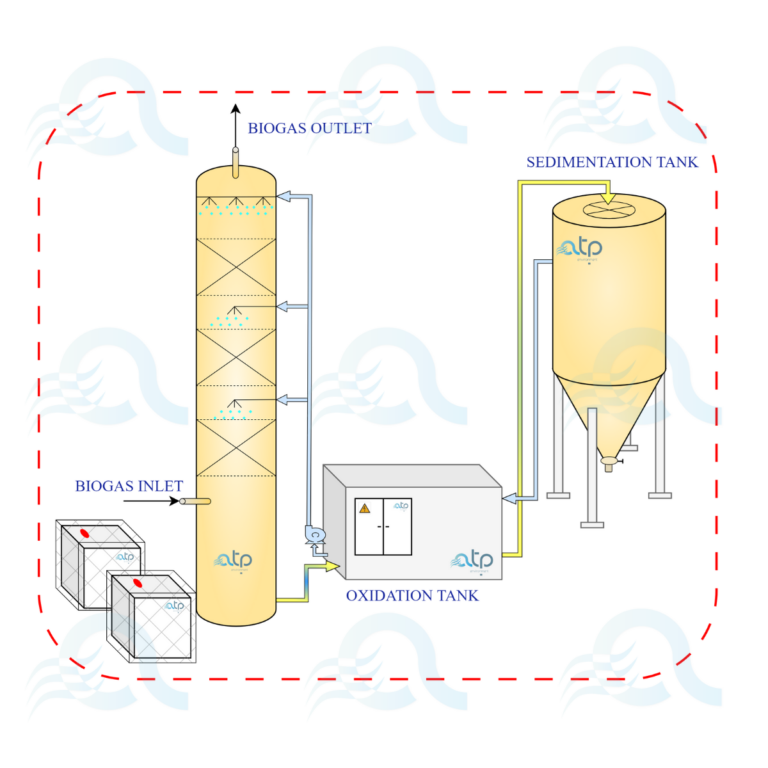
The desulfurization unit consists of a chemical scrubber combined with an oxidation tank and a sedimentation tank. The biogas enters from the bottom of the scrubbing tower and it is washed at low speed in counter-current with the washing liquid (NaOH) that moves through the packed bed. The solution then flows to the oxidation tank where a blower introduces air to promote oxidation; finally, the liquid is transferred to the sedimentation tank to let the sulfur settle at the bottom, and the liquid can be recirculated to the scrubber
Desulfurization of biogas is essential for removing hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), a toxic and corrosive compound produced during the anaerobic digestion of organic matter. High concentrations of H₂S can lead to equipment corrosion and pose significant health risks. To mitigate these issues, various treatment methods are employed:
Dry desulfurization:
- Impregnated activated carbon – utilizes activated carbon treated with chemicals like NaOH or KI to adsorb H₂S.
- Iron oxide-based media – materials such as iron oxide pellets or wood chips impregnated with iron oxide react with H₂S to form stable iron sulfides.
Wet desulfurization:
- Chemical scrubbing – involves washing the biogas with solutions that chemically react with H₂S to remove it.
- Biological scrubbing – employs microorganisms to oxidize H₂S into elemental sulfur or sulfate in a controlled environment.
In-situ treatments:
- Air or Oxygen Injection – introducing controlled amounts of air or oxygen into the digester promotes the activity of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria, reducing H₂S levels.
- Chemical additives – adding compounds like ferric chloride directly into the digestion process precipitates sulfides, thereby reducing H₂S formation.
Selecting the appropriate desulfurization method depends on factors such as H₂S concentration, biogas flow rate, and specific operational requirements. Effective removal of H₂S not only protects infrastructure but also ensures compliance with environmental regulations and enhances the safety and efficiency of biogas utilization.
Which problem can sort it out?
The desulfurizer scrubber filtration system is specifically engineered to address a range of environmental and operational challenges associated with the presence of hydrogen sulfide in biogas.
This technology effectively removes hydrogen sulfide, which is crucial for preventing corrosion in equipment, reducing unpleasant odors, and meeting stringent environmental regulations. By eliminating this harmful compound, the system enhances the quality of biogas, making it safer for use and reducing its overall environmental impact.
This advanced filtration solution is vital for industries relying on biogas, ensuring efficient, reliable, and eco-friendly operations
The use of a desulfurizer offers additional advantages:
- Greater energy efficiency: The presence of H₂S reduces the efficiency of the biogas combustion process. By removing sulfur, the fuel becomes cleaner, improving energy performance.
- Contribution to sustainability goals: The use of desulfurizers supports efforts to reduce environmental impact, helping to achieve sustainability objectives at national and global levels, in line with climate change agreements.
- Reduction in maintenance costs: By eliminating sulfur from exhaust gases, the formation of corrosive substances is reduced, which extends the service life of equipment and structures, lowering repair and replacement expenses.
- Reduction of unpleasant odors: Hydrogen sulfide is responsible for the characteristic “rotten egg” smell. A desulfurizer helps reduce unpleasant odors during the production and distribution of biogas, improving the local environmental impact.








![ISO 9001 [Italy] ISO 9001 [Italy]](https://atpenvironment.com/wp-content/uploads/elementor/thumbs/ISO-9001-Italy-1-e1734709424454-qysjxm32zf8e8mhshe2a1tecm8cbvnzg0wb4e904dc.jpg)